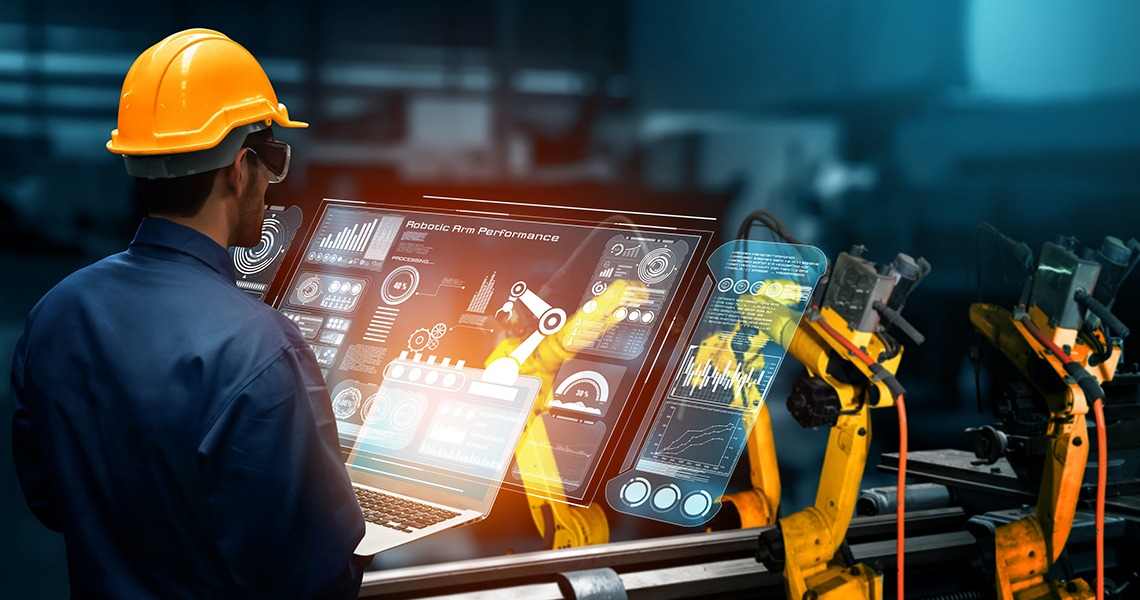
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the use of connected devices in factories to achieve a higher level of automation in industrial machines, which improves efficiency.
In a more technical definition, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the set of autonomous devices that connect via the Internet to different industrial applications, facilitating data collection, analysis and optimisation of production, improving efficiency and saving on costs generated during the manufacturing process.
According to Oxford Economics, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) impacts industries that account for around 62% of GDP in G20 countries, including Manufacturing, Energy and Food.
Differences between IIoT and IoT
The IoT, or Internet of Things, refers to everyday objects that can be connected to a network to exchange various data with other devices. When these objects are equipment that is used for industrial purposes, they are considered IIoT. The IIoT is therefore a part of the IoT.
Within the great heterogeneity of devices, some examples of IoT use by users can be lights, thermostats, blinds or locks that are connected, while those of the IIoT range from machinery to industrial ovens to production lines, among many others.
4Action, the IoT orchestration platform from Zerintia Technologies
4Action is Zerintia Technologies IoT orchestration platform that allows the integration of data generated by different sources of the industrial plant (such as Operational Technologies, Information Technologies and employees) for the detection of events in real time.
Based on this data and the application of configurable rules thanks to a rules engine, these trigger actions in response to these input events, involving employees, machinery and information systems.
4Action is currently in operation in several industrial companies, enabling their employees to make use of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).